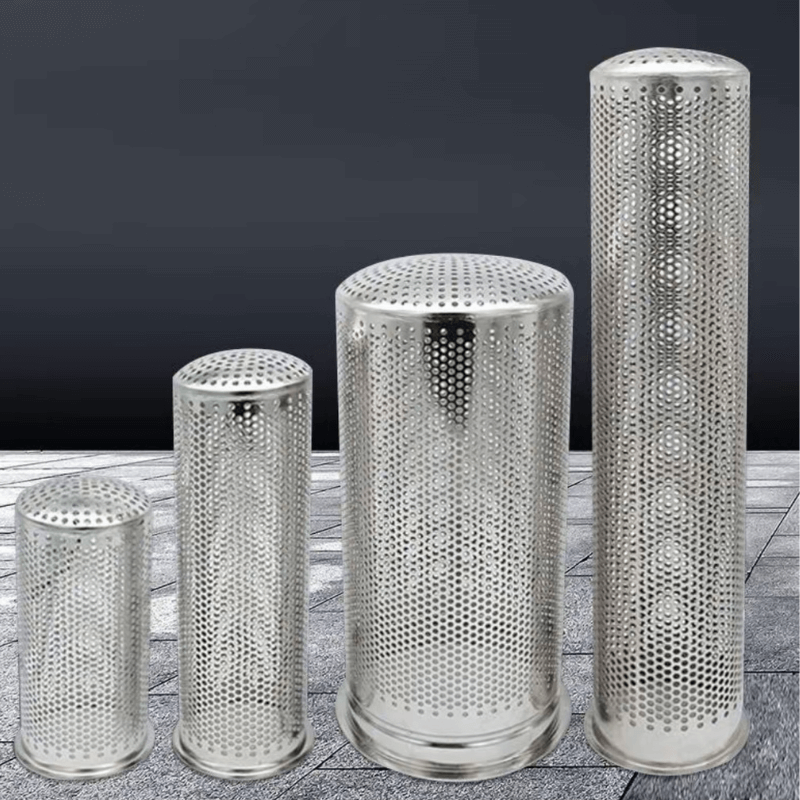
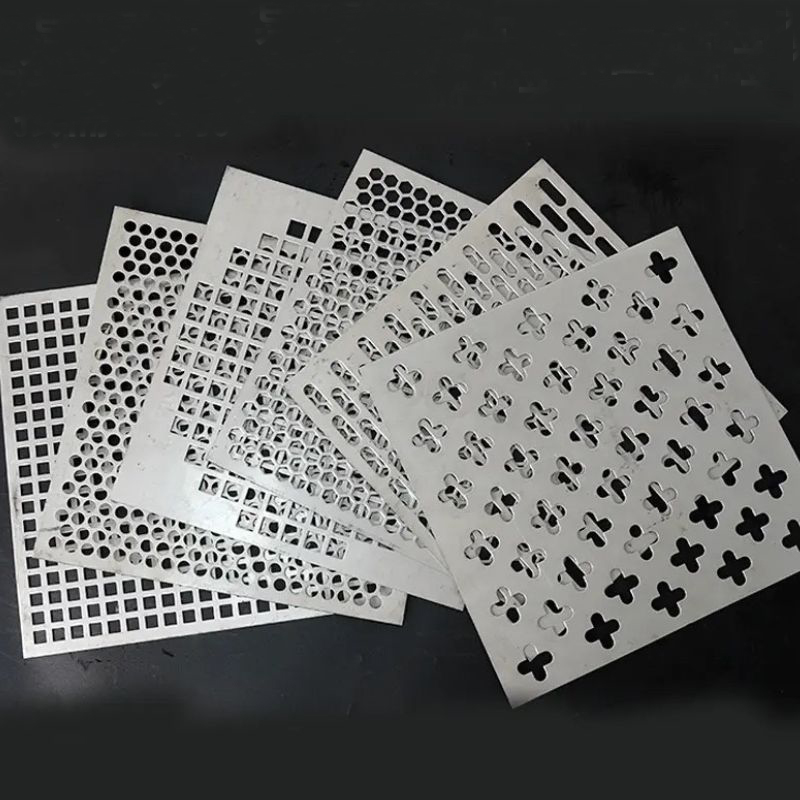
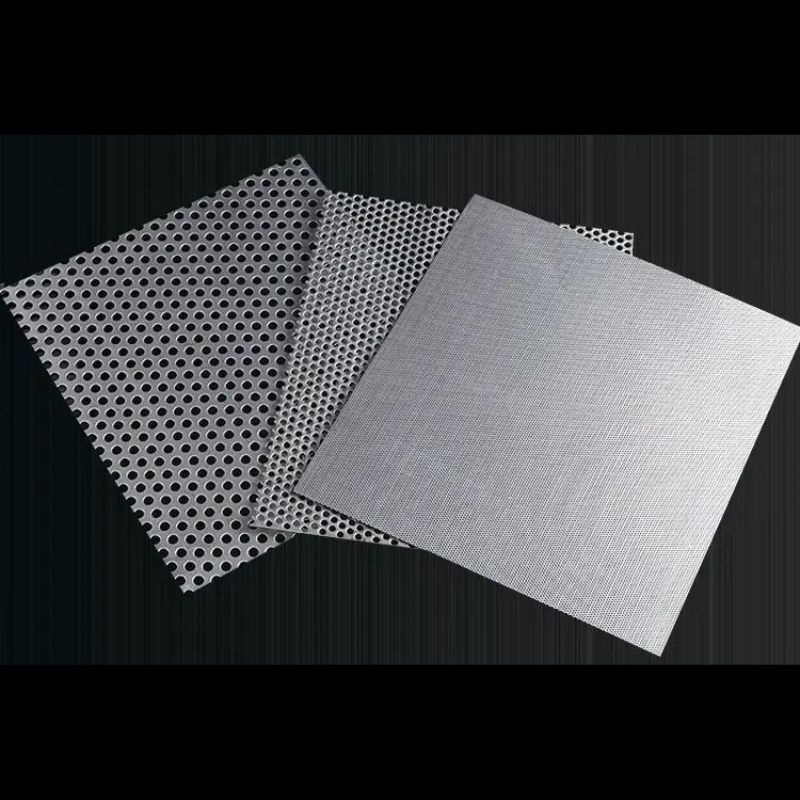
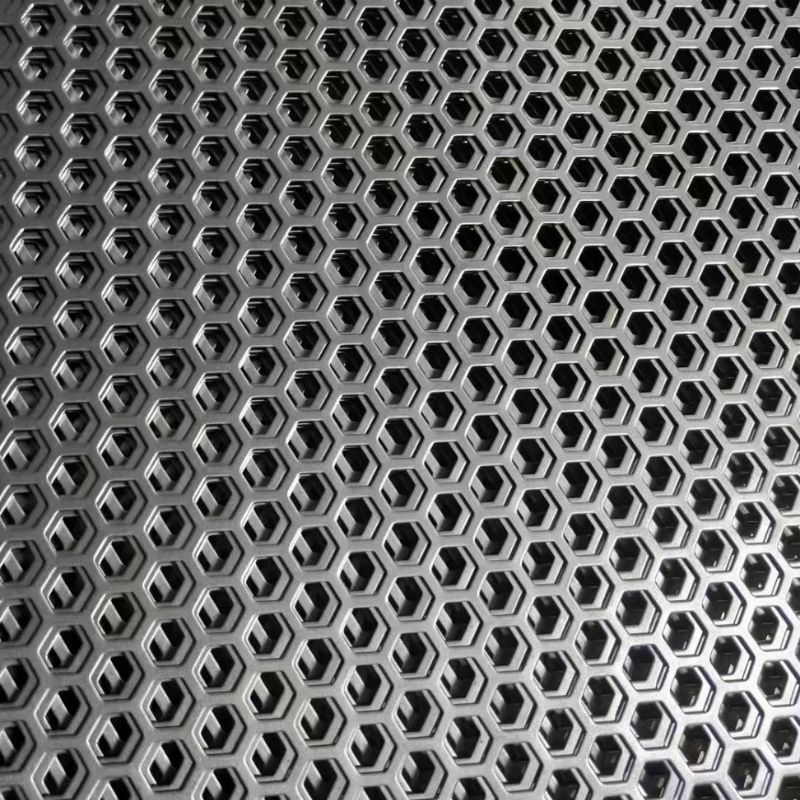
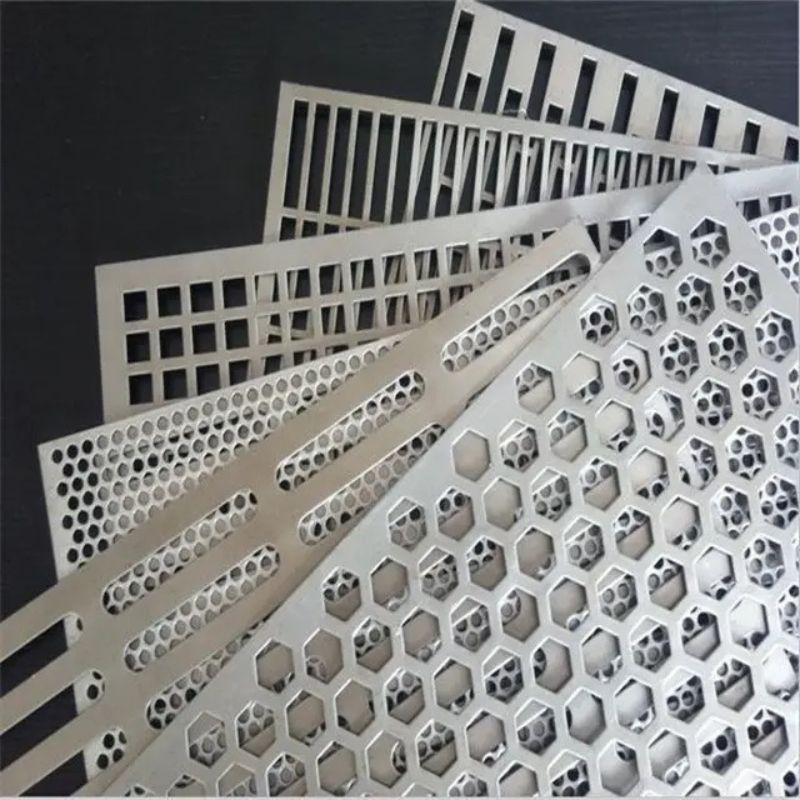
مقدمة عن صفائح الفولاذ المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة
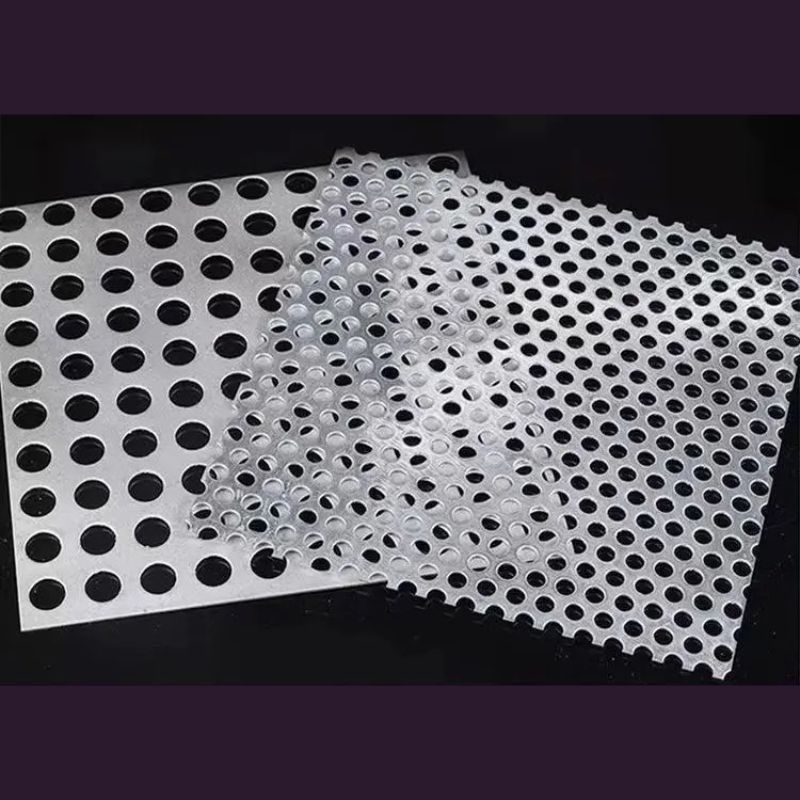
أ صفائح فولاذية مثقبة ذات ثقوب مستديرة هو نوع من الصفائح المعدنية التي تحتوي على سلسلة من ثقوب مستديرة مثقوبة بدقة مُرتَّبة إما بنمط مستقيم أو مُتَدَرِّج. مُصنَّعة من الفولاذ الكربوني، أو الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ، أو الفولاذ المجلفن، تعد هذه الأوراق من بين أكثر أنواع المواد المثقبة استخدامًا على نطاق واسع في مختلف الصناعات.
مع نسبة عالية من القوة إلى الوزن، وقدرات تهوية ممتازة، ومرونة واسعة في التصميميعد الفولاذ المثقب ذو الثقوب المستديرة حلاً أساسيًا لكل شيء بدءًا من اللمسات المعمارية إلى الترشيح الصناعي والحماية الميكانيكية.
أهم فوائد صفائح الفولاذ المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة
1. الحد الأقصى للمساحة المفتوحة
تسمح الثقوب المستديرة بـ نسبة المساحة المفتوحة الأكبر من الأشكال الأخرى، مما يجعلها مثالية لـ:
-
تدفق الهواء والتهوية
-
انتشار الصوت
-
انتقال الضوء
-
تصريف المياه
يمكن تخصيص المنطقة المفتوحة عن طريق التعديل قطر الثقب، والتباعد، واتجاه النمط.
2. قوة ومتانة ثابتة
إن المتانة المتأصلة في الفولاذ، جنبًا إلى جنب مع الثقوب الموحدة، تضمن سلامة هيكلية استثنائيةسواء في التطبيقات التي تتحمل الأحمال الثقيلة أو البيئات القاسية، الفولاذ المثقب يقاوم الصدمات والحرارة والتآكل - خاصة عند استخدام الأنواع المصنوعة من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ أو المجلفن.
3. مجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات
بسبب تنوعها، صفائح فولاذية مثقبة ذات ثقوب مستديرة يتم استخدامه في مجموعة متنوعة من الصناعات بما في ذلك:
-
العمارة والبناء
-
الزراعة وتجهيز الأغذية
-
السيارات والنقل
-
التصنيع والهندسة الميكانيكية
4. مرونة التصميم
يوفر تصميم الفتحة المستديرة خطوط نظيفة، وجماليات حديثة، وتنوع وظيفي. يتكامل بشكل جيد مع العناصر النفعية والزخرفية في التصميم.
التطبيقات الشائعة للصفائح الفولاذية المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة
1. الاستخدام المعماري والزخرفي
تُعد الألواح المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة هي المفضلة لدى المصممين لما يلي:
-
ألواح السقف والحواجز الصوتية
-
واجهات المباني والواقيات الشمسية
-
الأقسام الداخلية والكسوة
-
لافتات وميزات حائط مخصصة
إنهم يتوازنون وظيفة مع التعبير الفني، تقدم مزيجًا أنيقًا من الخصوصية والتحكم في الإضاءة وتدفق الهواء.
2. الاستخدام الصناعي والتصنيعي
في البيئات الصناعية، صفائح الفولاذ ذات الثقوب المستديرة مهمة في:
-
أنظمة الترشيح والغربلة
-
واقيات الماكينة والألواح الواقية
-
أحزمة النقل وصواني التجفيف
-
لوحات تقليل الضوضاء الصوتية
هُم ثقوب موحدة ومتانة عالية ضمان الأداء في ظل الظروف الصعبة.
3. التطبيقات الزراعية
يستخدم المزارعون ومصنعو الأغذية الفولاذ المثقب في:
-
أنظمة تجفيف البذور والحبوب
-
صواني الفرز
-
لوحات التهوية في مناطق الثروة الحيوانية
تعتبر الإصدارات المصنوعة من الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ مثالية لـ سلامة الغذاء ومقاومة التآكل.
4. السيارات والنقل
يتم دمج الفولاذ المثقب ذو الثقوب المستديرة في المركبات من أجل:
-
شبكات المبردات والدروع الحرارية
-
أغطية مكبرات الصوت وعزل الصوت
-
مكونات التهوية
تساعد المادة على تقليل الوزن مع الحفاظ على القوة وتدفق الهواء.
خيارات المواد للصفائح المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة
1. الفولاذ الكربوني
-
اقتصادي
-
قوة وصلابة عالية
-
مناسب للبيئات الداخلية أو المحمية
-
يمكن طلائها أو طلائها بالمسحوق
2. الفولاذ المجلفن
-
طلاء الزنك لمقاومة التآكل
-
مثالي للمناطق الخارجية أو المعرضة للرطوبة
-
عمر طويل وصيانة منخفضة
3. الفولاذ المقاوم للصدأ (الدرجات 304، 316، وما إلى ذلك)
-
مقاومة ممتازة للتآكل والمواد الكيميائية والحرارة
-
مناسب للبيئات الغذائية والطبية
-
متانة عالية ونظافة عالية
أنماط ومواصفات الثقوب المستديرة
أقطار الثقوب
تتراوح الأحجام القياسية من 0.5 مم إلى 25 مم أو أكثرحسب الاستخدام. تُستخدم ثقوب أصغر لـ ترشيح دقيق أو شبكات مكبرات الصوتفي حين أن الثقوب الأكبر مناسبة لـ التهوية أو الفحص الثقيل.
تباعد الثقوب (الملعب)
المسافة بين الثقوب ضرورية لتدفق الهواء ومتانته. تشمل التصميمات الشائعة ما يلي:
-
النمط المتدرج (60 درجة/45 درجة): يوفر أقصى قدر من المساحة المفتوحة والجاذبية البصرية
-
النمط المستقيم: من السهل محاذاتها مع الهياكل الأخرى؛ تستخدم لأغراض ميكانيكية أو صناعية
سمك الورقة
متوفر في مجموعة متنوعة من السماكات، تتراوح عادةً من من 0.5 مم إلى 10 مم. يتم استخدام صفائح أكثر سمكًا حيث قوة تحمل الحمل ضرورية.
خيارات التشطيب
-
طلاء المسحوق: يضيف اللون ومقاومة التآكل
-
الجلفنة بالغمس الساخن: ينشئ طبقة سميكة من الزنك للبيئات القاسية
-
التلميع أو التنظيف بالفرشاة: يعزز المظهر والنظافة
-
الأكسدة (للألومنيوم):اختياري للمواد الهجينة
يتم تحديد التشطيب في كثير من الأحيان من خلال التعرض البيئي والاحتياجات الجمالية والميزانية.
خدمات التخصيص
تقدم الشركات المصنعة الرائدة خدمات التثقيب المخصصة مشتمل:
-
أحجام الثقوب غير القياسية
-
أنماط التباعد المتغيرة
-
أحجام وأشكال الأوراق المخصصة
-
القطع بالليزر واللكم باستخدام الحاسب الآلي
-
التشكيل واللحام وتشطيب الحواف
تساعد هذه التخصيصات على تلبية المتطلبات الهندسية والمعمارية الدقيقة.
نصائح التركيب والصيانة
-
يجب التعامل دائمًا باستخدام معدات الحماية لتجنب الإصابة من الحواف الحادة
-
استخدم أدوات التثبيت المناسبة للمادة والبيئة
-
قم بالتنظيف بانتظام لمنع تراكم الغبار أو العوامل المسببة للتآكل
-
فحص دوري بحثًا عن أي علامات للتآكل، وخاصة في الاستخدامات البحرية أو الخارجية
اعتبارات الشراء
عند اختيار صفائح الفولاذ المثقبة ذات الثقوب المستديرة، ضع في اعتبارك ما يلي:
-
حجم الحفرة والمساحة المفتوحة بناءً على متطلبات تدفق الهواء أو الضوء أو الصرف
-
سمك الورقة ونوع المادة على أساس القوة ومقاومة التآكل
-
تخطيط النمط لتتناسب مع القصد البصري أو الوظيفي
-
الكمية والأبعاد لضمان التثبيت السلس
تأكد من أن المورد الخاص بك يوفر المواصفات الدقيقة والشهادات لضمان الجودة.

 casssia@yoyimachinery.com
casssia@yoyimachinery.com